Overview
The following great article is helpful for us when configuring Azure Front Door in front of API Management to accept only traffic from Azure Front Door at API Management.
Integrate Azure Front Door with Azure API Management - Microsoft Tech Community
I would like to add information in case of using Application Gateway.
Query from customer
As always, I received the following query from my customer.
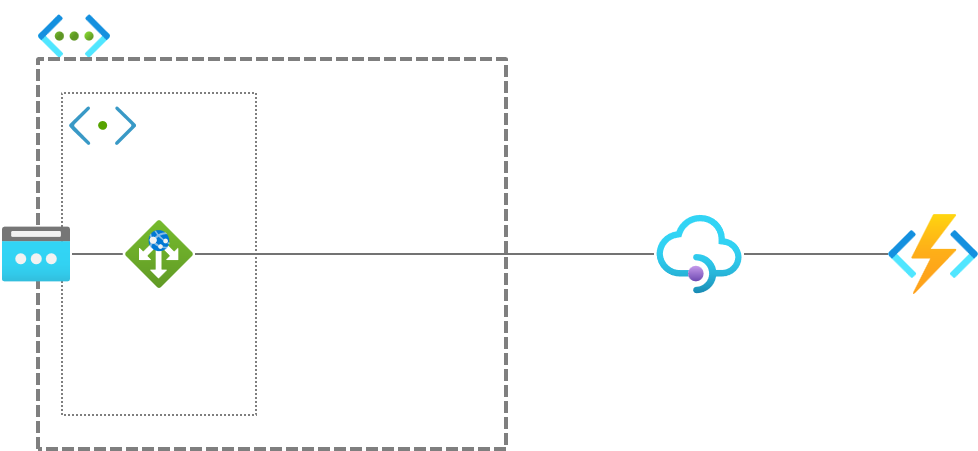
Now they are trying to use Azure API Management and Azure Functions for backend services to expose APIs. They plan to use Application Gateway as a web application firewall (WAF) in front of API Management. As they don't use either premium SKU or developer SKU, however, their API Management instance is not permitted to access VNet. In this situation, how do they configure each component behind Application Gateway to avoid accessing it from Internet directly?
I illustrated their requirements.
If they used premium SKU for both API Management and Azure Functions, they would not have to worry about that (as these services can access VNet when using Premium SKU). However, this customer uses Consumption SKU for Azure Functions, and Basic SKU for API Management.
Solution sample
Note: This is an example and is not the only one solution.
- As Application Gateway is already configured for public access, assigned public IP address is used to communicate API Management instance. Therefore, NAT Gateway for communication with API Management instance is optional (not required).
- Configure API Management instance to accept only traffic from Application Gateway instance. Along with source IP restriction, subscription key is also acceptable.
- Configure Function app to accept only traffic from API Management instance. Along with source IP restriction, API host key and authentication are also acceptable.
1. Application Gateway
As I mentioned above, public IP address is already assigned to Application Gateway instance and the IP address is also used for outbound communication. Therefore, we don't have to do anymore.
We can create a NAT Gateway, assign another public IP address (or IP address prefix) to the gateway, and deploy it to a subnet for outbound connection, of course. In this case, public IP address assigned to NAT Gateway is used to communicate with the API Management instance.
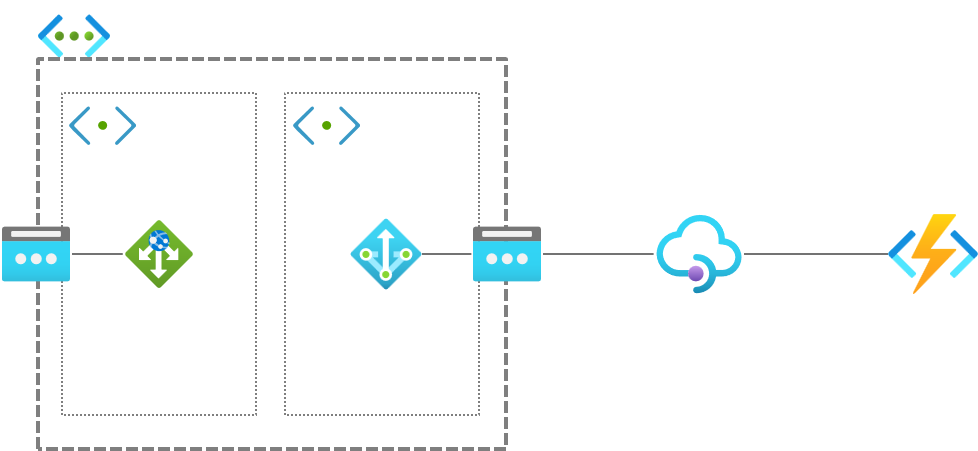
2. API Management
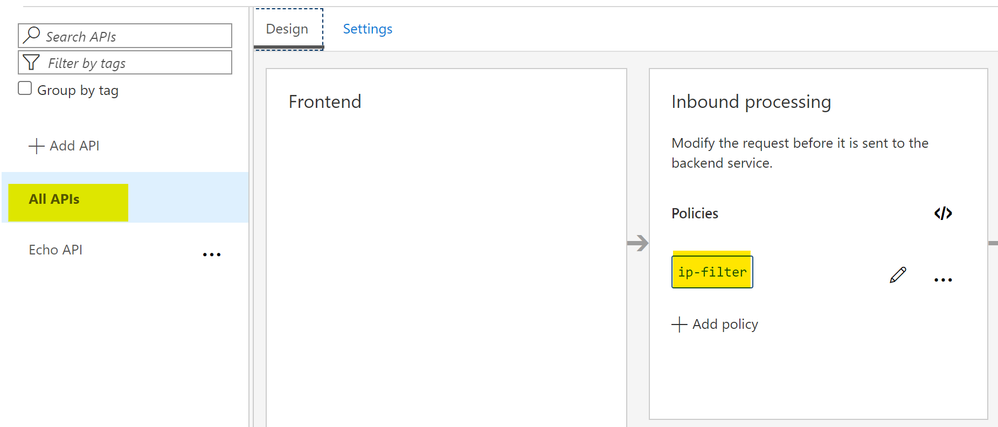
To accept only traffic from the Application Gateway instance, we can use ip-filter policy to restrict source IP in API Management.
IP Filter policy
Azure API Management access restriction policies | Microsoft Docs
This policy should be defined in global scope as we have to check all traffics to the API Management instance.
Global scope
How to set or edit Azure API Management policies | Microsoft Docs
IP address(es) assigned to Application Gateway instance or NAT Gateway are filled in this field as permitted source IP address(es).
Policy configuration is as follows.
<policies>
<inbound>
<ip-filter action="allow">
<address>xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx</address>
</ip-filter>
</inbound>
<backend>
<forward-request />
</backend>
<outbound />
<on-error />
</policies>
We can also use original request IP addresses to filter requests through Application Gateway. For more details, check the following URL.
Enforcing using subscription key along with source IP address restriction would be much more strong restriction. When adding subscription key, configuration of HTTP header in Application Gateway is required.
3. Function app
In case of Function app, the following configuration should be done to avoid direct connection from the Internet.
- IP address restriction
Configure to accept only traffic from Public IP address assigned to the API Management instance. - Authentication
Configure authentication in Function app to accept only accesses from resources in the same Azure AD tenant. - Host key enforcement
Authorization level should be set tofunction.
IP address restriction and authentication would be sufficient, using host key along with them would be much better. In this section, I describe how to configure IP address restriction and authentication in Function app. Both configurations are the same as in case of App Service.
a) IP address restriction
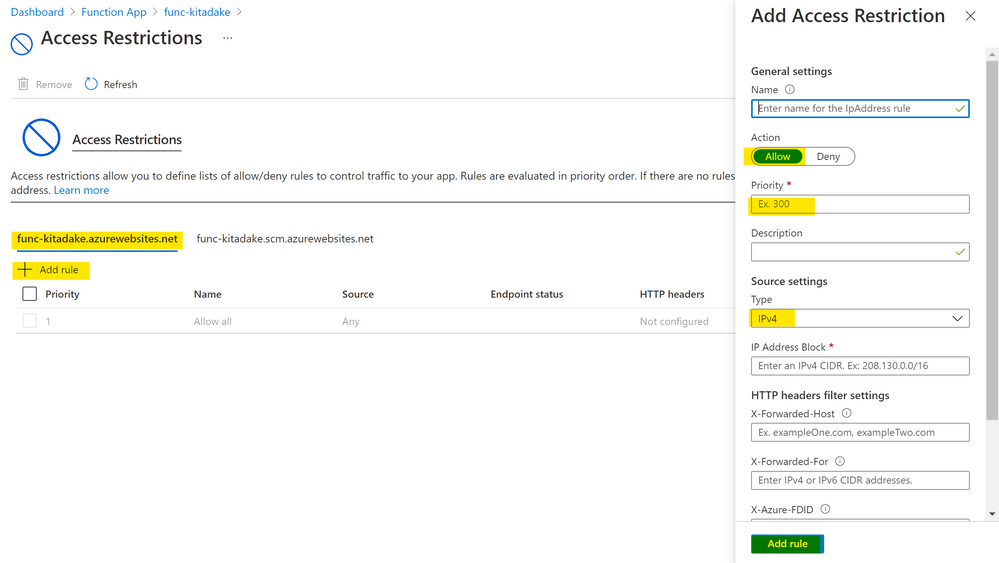
Settings > Networking > Incoming Traffic and click "Access restriction".
Click "+Add rule" on a tab whose name does not contain "scm".
Specify the following properties in the "Add Access Restriction" window pane.
- Rule name
- Action (
Allow) - Priority (any value is okay)
- Description (optional)
- Source settings
- Type (
IPv4)
Note: Service tag is not applicable in this case. Indeed we can choose the service tagApiManagementorApiManagement.{region}, but these represents source IP addresses used for administrative traffic when deploying artifacts to API Management instance. For more details, check the following URL.
Available service tags
Azure service tags overview | Microsoft Docs
- Type (
- IP Address block (specify public IP assigned to API Management instance)
Click "Add rule" button to complete entering all properties.
b) Authentication
These steps are required to configure authentication in both Function app and API Management.
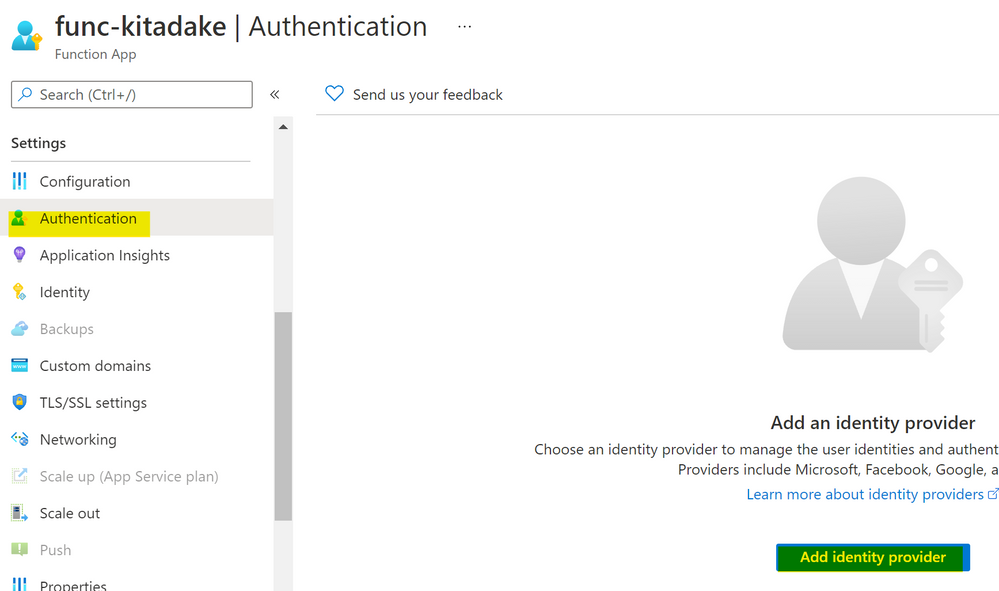
Function App
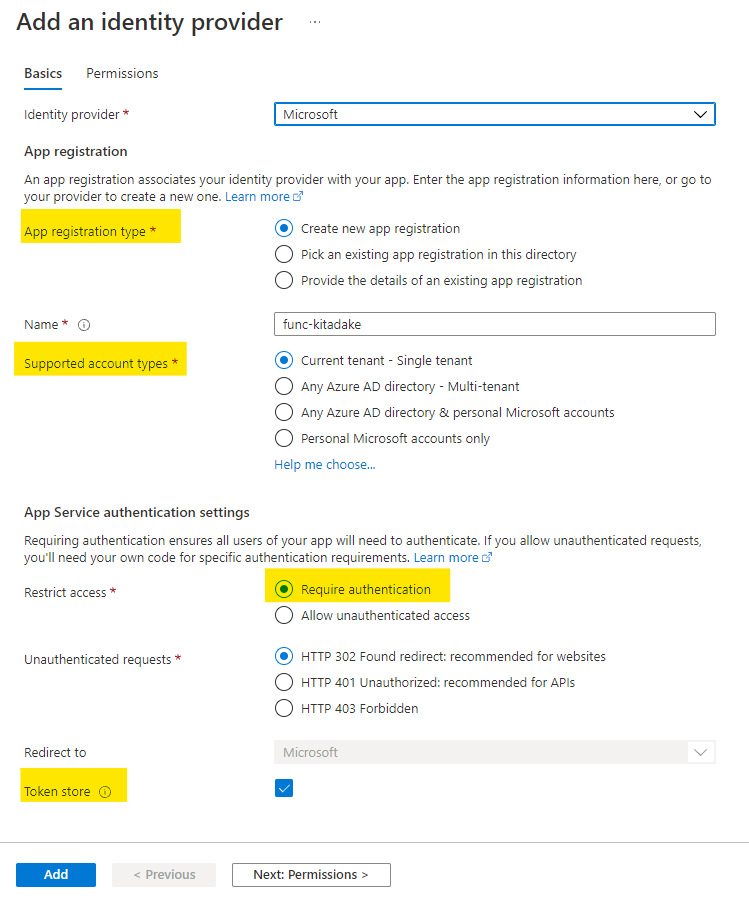
Settings > Authentication and click "Add identity provider".
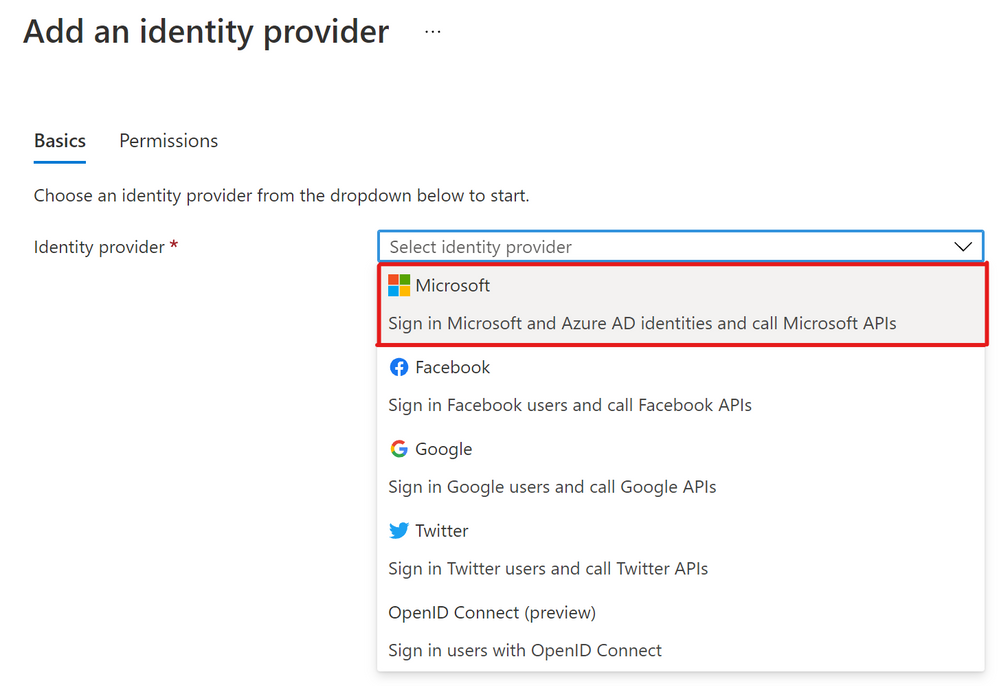
Next, choose "Microsoft" for identity provider to authenticate identities against Azure AD.
In "App registration", you can choose either registering your application to Azure AD or picking the existing application. In "Restrict access", choose "Require authentication" and enable token store (enabled by default). And click the button "Next: Permissions >".
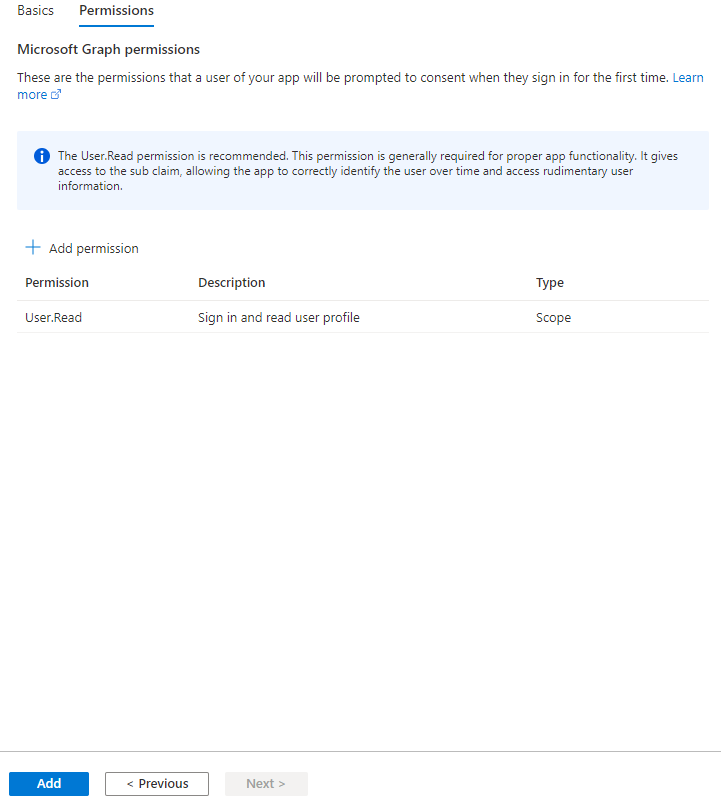
In "Microsoft Graph permissions", leave the default configuration and click "Add".
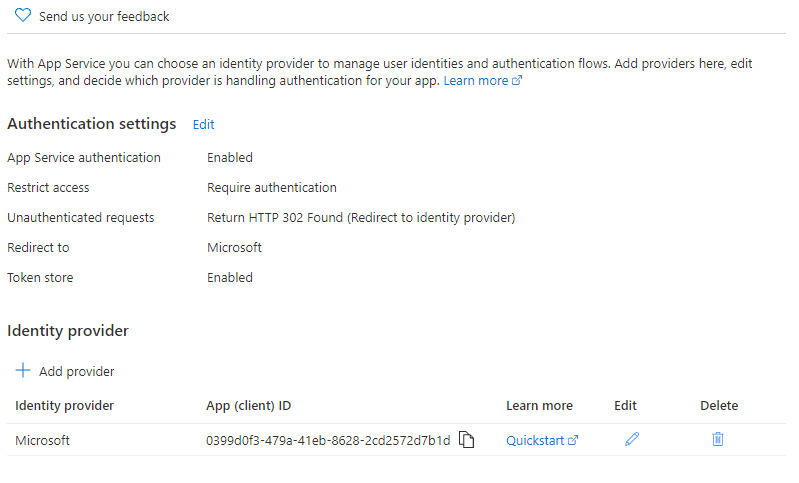
The following screen should appear after entry is completed. If you register application to Azure AD in the previous step, you can find client ID for the Function app. This client ID is required for authentication at API Management instance. (Note: this client ID has been already disabled.![]() )
)
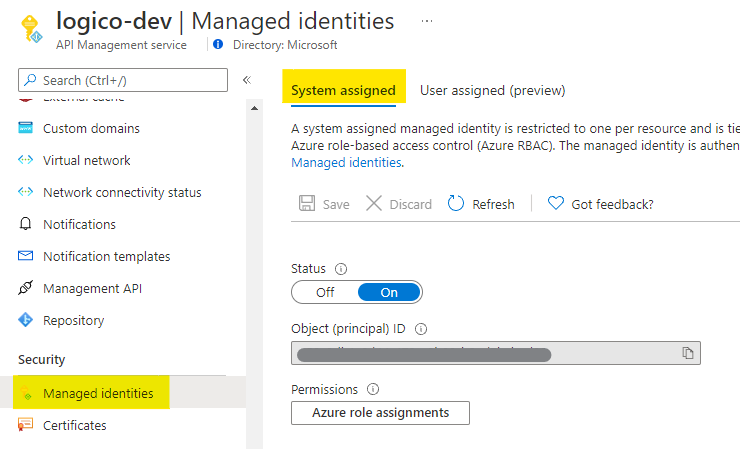
API Management
Security > Managed identities, and enable system-assigned managed identities of the API Management instance. we use this identity for authentication.
Next, APIs > APIs and choose not operation scope but API scope, and add authentication-managed-identity policy to inbound pipeline. Configuration of this policy is as follows.
<policies>
<inbound>
<base />
<authentication-managed-identity resource="0399d0f3-479a-41eb-8628-2cd2572d7b1d" />
</inbound>
<backend>
<base />
</backend>
<outbound>
<base />
</outbound>
<on-error>
<base />
</on-error>
</policies>
That's it!
4. Test
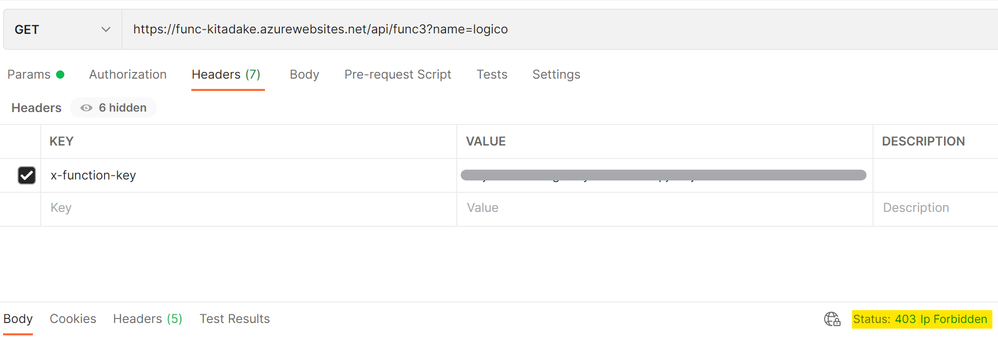
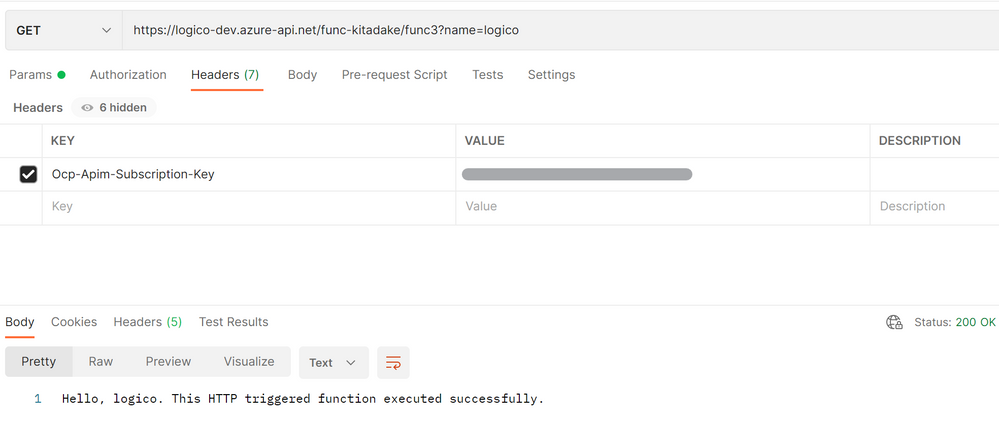
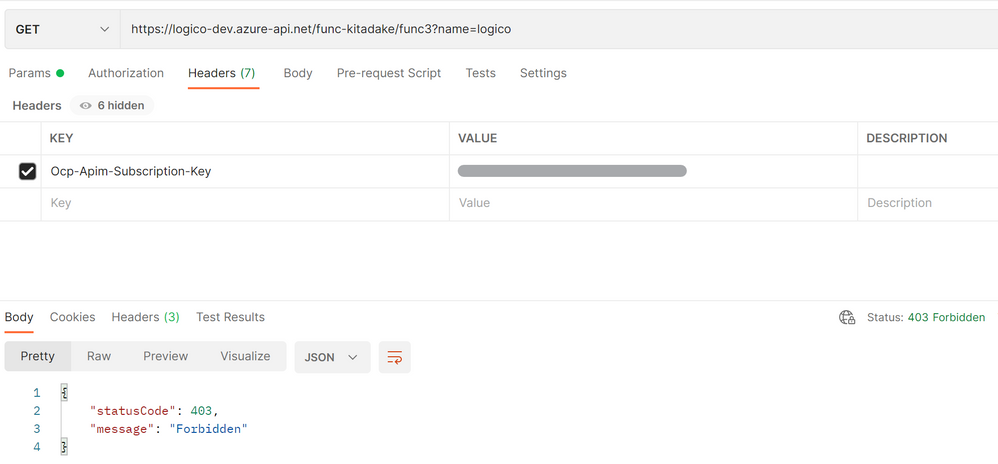
When invoking Function app directly, the app returns 403 due to IP address restriction.
When calling an API backed by Function app via API Management (with IP address restriction disabled on API Management), the API returns 200 with response body.
Note: you can pass subscription key to API Management in the form of query parameter (subscription-key) or HTTP header (Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key).
Next, when calling the API directly with IP address restriction enabled on API Management, it returns 403 .
At last, when calling the API via Application Gateway, it returns 200 with response body. (in this case, HTTP instead of HTTPS is used for testing purpose.)
How about Azure Front Door?
In case of Front Door, we can add API Management instance(s) in backend pool(s).
IP addresses Front Door uses for backend communication are different from front-end IP address(es) assigned to Front Door and the former is packed into the service tag AzureFrontDoor.Backend. However, when filling IP addresses in API Management ip-filter policy, the following limitation exists and additional tasks are required.
- API Management
ip-filterpolicy cannot accept any service tags. Therefore, we have to add all IP addresses packed in the service tag. - IP addresses contained in service tags are subject to change without notification. Indeed we might automate the task to download JSON file containing service tags, retrieve IP addresses, and update IP addresses in
ip-filterpolicy. However, some might think that its cost is expensive...
In some circumstances, access restriction using X-Azure-FDID might be reasonable. However, we keep in mind that we cannot use only X-Azure-FDID to restrict access from other services than Front Door strictly. The best solution to accept only traffic from Front Door would be Private Link Service, which is available in Front Door Standard/Premium SKU, but this service does not support API Management as of now.
Summary
My customer understood my proposal mentioned above, and they followed my proposal to configure their environment. In case of Azure Front Door, cost for IP address restriction is expensive as API Management ip-filter policy accepts only IP address(es) instead of service tag AzureFrontDoor.Backend. Simply using X-Azure-FDID is less expensive but this does not work for some cases.