Hello,
It has been a while since Raven, and I have blogged on security. My little buddy Raven (miniature Schnauzer) has been dealing with genetic back problems that have made it difficult to run or jump, so her days of roaming the yard and scaring off squirrels has been curtailed.
This past summer I was able to spend a lot of time in my backyard with Raven quietly resting alongside me. Raven has never given up on protecting the yard, but she needs help from me to find the intruders. She lays there quietly but when I say “Squirrel” and point, her back problems vanish temporarily as she vanquishes the little critter (don’t worry she never gets close to one).
As I initially sat and work on the technical topic of this blog, it dawned on me how much Raven needing help finding intruders and what Microsoft Sentinel (Formerly Azure Sentinel) can provide to our customers. Microsoft Sentinel is the alerting mechanism that finds the anomalies in your environment and can alert you to go evict them.
Windows Event Forwarding (WEF) isn’t something new, I believe it has been around for more than 20 years, but the ability to query has never been its strong point, plus storage can be an issue. Having the ability to get access to all of the enterprises Windows Event logging data without having to load a client (WEF is built into the o/s) has two major advantages.
No cost
No agent management
Imagine a customer with close to 200,000 endpoints and having to maintain the installed client base, that could be a real headache and client costs are very high (I am working with such a scenario). A WEC server can’t have that large of a number of clients so it has to be split out, and I have been asked “how many clients could connect to a single WEC server?” There is no precise answer to that question. Since there are many factors that enter into that question. Size of WEC server, amount of traffic being sent,… I have seen that the number of a clients that a WEC server can handle, could go as high as 10,000 clients but again the environment factors enter into this.
Once one or more WEC server have been stood up then you will need to add an “Azure Arc” connection to Azure, so Microsoft Sentinel can “Connect” to the WEC server. The Microsoft Sentinel connector “Windows Forwarded Events (Preview)” requires AMA, as it is not supported for MMA, and AMA requires the deployment of Azure Arc.
This will then provide the customer complete access to the logs from the hosts that exist outside of Azure (On-Premises, AWS, GCP for example) that were aggregated with WEF.
Below I have walked through the steps needed to help deploy a WEF to Microsoft Sentinel infrastructure.
Windows Event Forwarding Log Collector to Microsoft Sentinel Rollout
There is no need to load an agent on every device to capture the Windows Security Event Logs from your on-premises Windows workstations & servers. Windows hosts already have this built into the operating system. To capture the events without having to load the Azure Monitoring Agent (AMA) the Windows Event Forwarding process can be used to send logs to a “Windows Event Collector” (WEC). The WEC will then need the AMA loaded to send the events to a Log Analytics Workspace (LAW) that is monitored by Microsoft Sentinel.
Note: Microsoft Sentinel must be enabled/deployed prior to the deployment of the AMA agent.
From a high-altitude view:
- Deploy Microsoft Sentinel
- Build a Windows Event Collector (WEC) server to host the security event logs from client (source) computers
- Create a Group Policy to define where the clients are to request the logs and events (Subscription), they are to send to the WEC
- Create a subscription on the WEC to define what logs and events to receive
- For on-premises WEC server(s), enroll it/them in the Azure Arc service
- Add the Microsoft Sentinel, “Windows Forwarded Events (Preview)” connector
- Define the WEC hosts
- Define the “Forwarding Event Logs” log to collect from
- Browse/Query (KQL) the LAW for Security Events
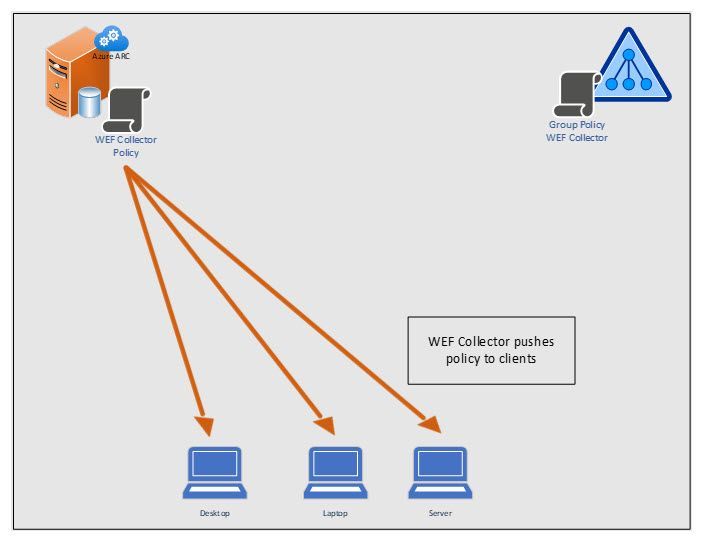
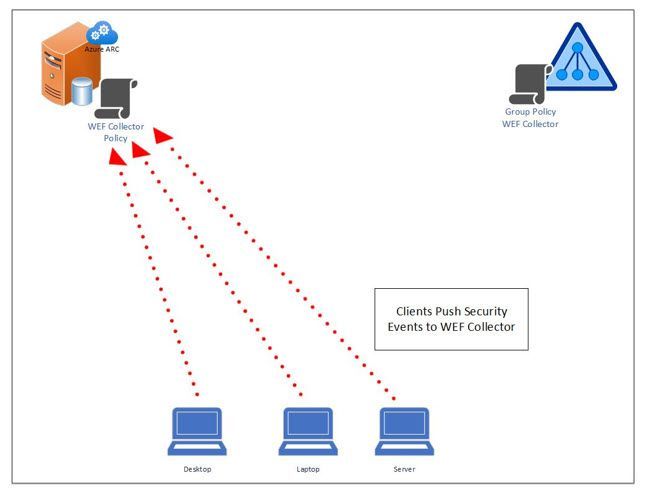
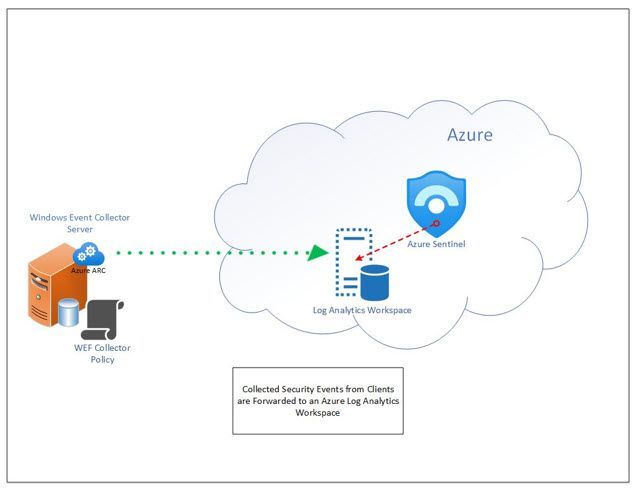
High Level Steps in Graphic Format
Create and Push GPO To Clients So They Can Find the WEF Collector
Clients Request WEF Policy from WEF Server
WEF Collector Pushes Policy to Clients
Clients Continuously Push Security Events to WEF Collector
Collected Security Events are Continuously Forwarded to the Azure Log Analytics Workspace
Building a Windows Event Collector
This is a resource requirement. The size of the host will depend on the number of source clients and logs being forwarded to the WEC.
“You deploy EventLog Forwarding in a large environment. For example, you deploy 40,000 to 100,000 source computers. In this situation, we recommend that you deploy more than one collector that has 2,000 cleitns to not more than 4,000 clients per collector.
Note: AMA can handle up to 5,000 EPS, but be aware that it is important to have enough WEC servers as if the limit of EPS is reached the agent won’t be able to handle the load.
Additionally, we recommend that you install at least 16 GB of RAM and four (4) processors on the collector to support an average load of 2,000 to 4,000 clients that have one or two subscriptions configured.
Fast disks are recommended, and the ForwardedEvents log can be put onto another disk for better performance.
The memory usage of the Windows Event Collector service depends on the number of connections that are received by the client. The number of connections depends on the following factors:
- The frequency of the connections
- The number of subscriptions
- The number of clients
- The operating system of the clients
For example, for the default values of 4,000 clients and five to seven subscriptions, the memory that is used by the Windows Event Collector service may quickly exceed 4 GB and continue to grow. This can make the computer unresponsive.”
Best practice of configuring EventLog forwarding performance - Windows Server | Microsoft Docs
Create a Group Policy Object (GPO) and link it to an Organization Unit (OU)
WEF uses WINRM, which uses ports 5985 for http or 5986 for https. Ensure that you have the winrm service running on clients before you start capturing traffic. Winrm is started by default on Windows Server 2008 and beyond.
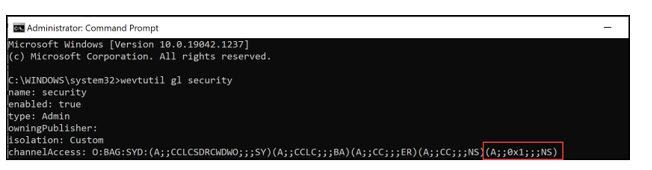
If the goal is to capture the Security event logs as one of the logs (In our demo we will need to capture the Security Event Logs), then it will be required to grant the “Network Service” access to the Security event log, by default access is denied. From an Active Directory domain machine, run the following command, from an elevated command line:
wevtutil gl security
This will list out the ACL’s defined on the Security Event Log. Look for “channelAccess” the "O:BAG:SYD:" is where the permissions on the log are stored. Copy from the O through the last parenthesis and paste it into Notepad. If there isn’t a (A;;0x1;;;NS) on the end like the example below, then append that on to the line in Notepad. This last part provides the Network Service (NS), access to the Security Event log.
Start up Group Policy Management Editor
There are 2 settings that will need to be added, to point the clients to the WEC server
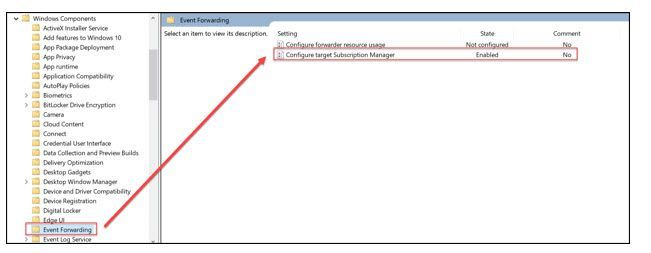
Computer>Policies>Admin Templates>Windows Components>Event Forwarding>Configure target subscription manager
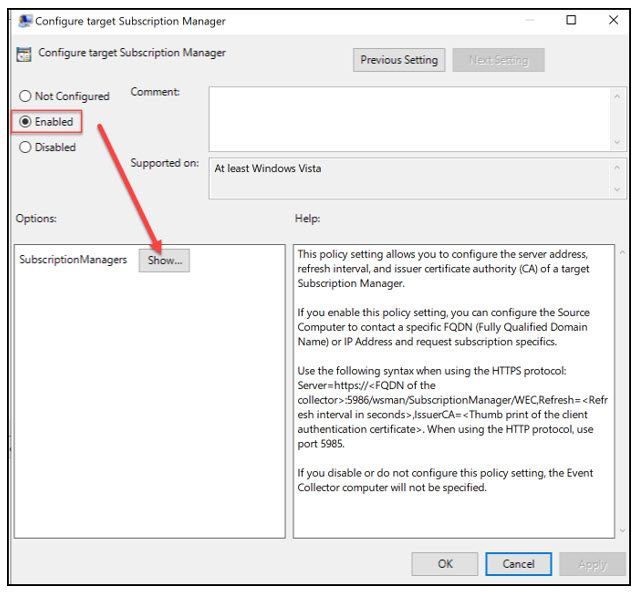
This will need to be updated with the address of your WEC server in the format shown below:
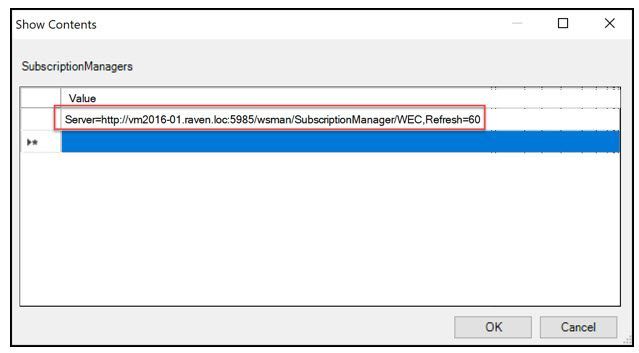
Server=http://fqdnofWECserver:5985/wsman/SubscriptionManager/WEC,Refresh=60
Replace the red highlighted area with the fqdn of the WEC server.
Note: “Server=” is needed in the line defined above
The refresh interval on the end indicates how often clients should check in to see if new subscriptions are available. In this example 60 seconds is extremely chatty, but during testing you only have to wait 1 minute for updated configuration. Setting to hourly (Refresh=3600) in production should work just fine.
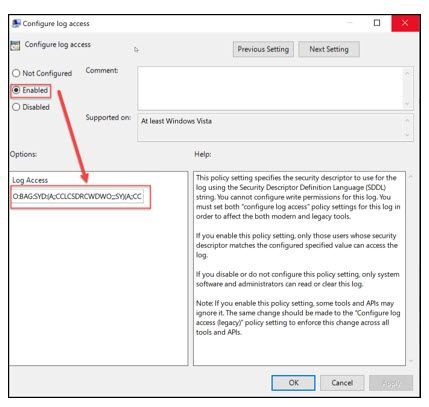
Once the defined WEC has been completed, the Network Service needs to be granted access to the Security Event Log. This step is not needed if you won’t be reading that log file.
Computer>Policies>Admin Templates>Windows Components>Event Log Service>Security> Configure log access
From a previous step where the Security Event log permissions were built and stored in Notepad, this value will now be updated in the GPO.
Note: This will replace any previous settings on this Event Log, so just be aware of this update.
Once this GPO has been built, it will be up to the admin to decide how to apply the policy to the workstations/servers so they can check in with the WEC server to get the subscription definition.
Create a WEC subscription
Now that client GPO has been defined a subscription needs to be built to tell these clients what logs and Events should be “Forwarded”.
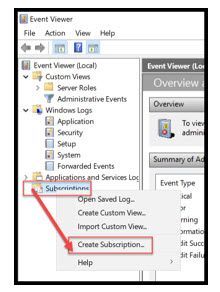
From the WEC server, start up “Event Viewer”.
Right click on “Subscriptions” and select “Create Subscription...”.
- “Subscription name:” Enter a unique name for the subscription (try to avoid spaces)
- “Description:” is optional
- “Destination log:” Select the log file “Forwarded Events”
- Select “Source Computer Initiated”
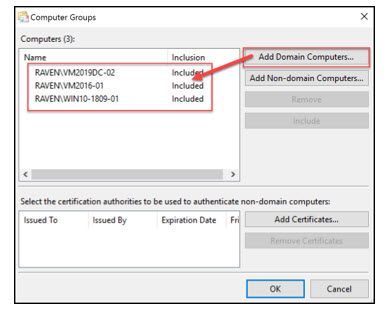
- Click on “Select Computer Groups…”
Select the “Add Domain Computers” button and walk through the Active Directory (AD) picker to populate the Computers to be added. In the example below, there are just individual machines but AD groups can also be used. Once all objects have been selected click the “Ok” button”
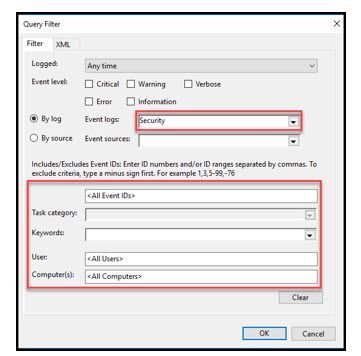
From the “Subscription Properties” main page, click on the “Select events” button.
The “Query Filter” page allows the admin of the filter the ability to only forward events interested in capturing. This filter will be used by all client subscribers that are forwarding events. These events will all be sent to the WEC server. If the admin would like the WEC server to capture all events but filter this list before sending to Microsoft Sentinel, there is a second filter definition on the Microsoft Sentinel connector.
Note: Events are continuously sent to the WEF collector
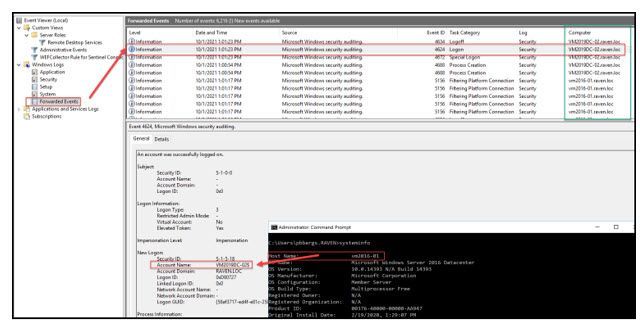
Once filtering has been completed, select “Ok” and select “Ok” again on the Subscription properties page.
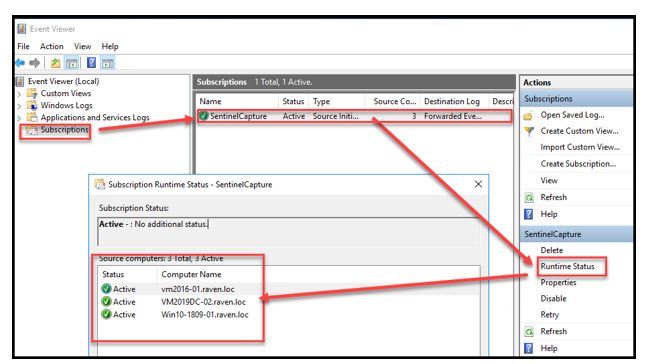
Waiting approximately 15 minutes (After the GPO has applied to the clients), the “Forwarded Events” log should begin to populate from subscribers to the WEC subscription.
If you look closely at the screen capture below you will see that the “Forwarded Events” log resides on vm2016-01 (DOS prompt), yet the reporting in the event itself belongs to VM2019DC-01.
Enroll WEC server(s) into Azure Arc services
In order to capture events within Microsoft Sentinel, there has to be a connection to the Log Analytics workspace that Microsoft Sentinel monitors. To do this we need to enroll our WEC server into Azure Arc. This is completed by installing the Azure Monitor Agent.
- Log onto the Azure portal:
https://portal.azure.com - From the search portal enter, “Servers - Azure Arc” and select this to go to the “Servers - Azure Arc” blade.
- Click on “+ Add”
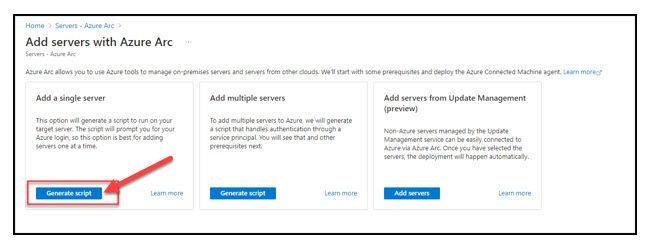
- For this initial trial rollout, select the “Generate Script” from the “Add a single server” box.
- Select “Next”
- Complete the Resource Details and click on “Next”
Note: In the example from my lab below, I am using a “Public” endpoint. I would strongly encourage organizations to not expose ANY log files on the public internet!
- Enter any required “Tags” for your organization and select “Next”
- Select the “Download” button
- Select the “Copy” button
- The “Download” button will probably be blocked by your organization
- From the on-premises WEC collector desktop, open a script editor (Notepad for example) and paste the contents of the clipboard and save it as “WEC-Sentinel.ps1”.
- Open an elevated PowerShell command prompt
- Change directories to where you saved “WEC-Sentinel.ps1”
- Execute the script: .\WEC-Sentinel.ps1
- You will be prompted to sign into a web browser and enter a code
- Follow the on screen prompts to logon and approve the joining of this machine to Azure Arc
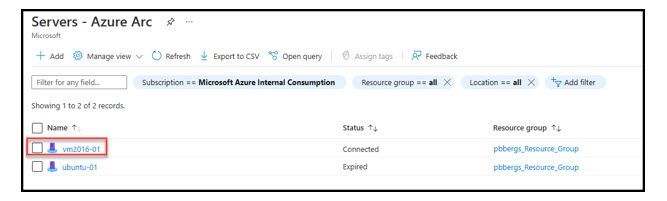
- Move back to the “Servers – Azure Arc” blade, hit refresh and the newly onboarded host should now be a part of this subscriptions “Azure Arc” as seen with the Data Collector (“vm2016-01”) below.
Add the Microsoft Sentinel, “Windows Forwarded Events (Preview)” connector
Once events are being collected, the events now need to be imported into a “Log Analytics Workspace” (LAW) for Sentinel to be able to monitor and report on them.
- Log onto the Azure portal:
https://portal.azure.com - Select Microsoft Sentinel
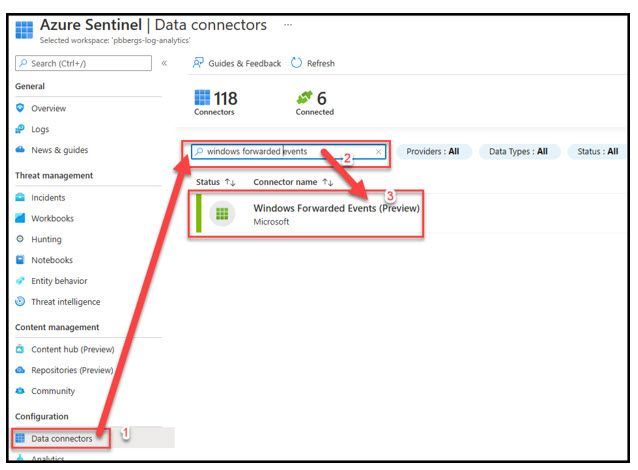
- Select the “Data Connectors” blade
- Select the LAW that you would like to aggregate events to from the WEC
- Enter “Windows Forwarded Events” in the “Search by name or provider” box
- Click on “Windows Forwarded Event”
- Select “Open connector page”
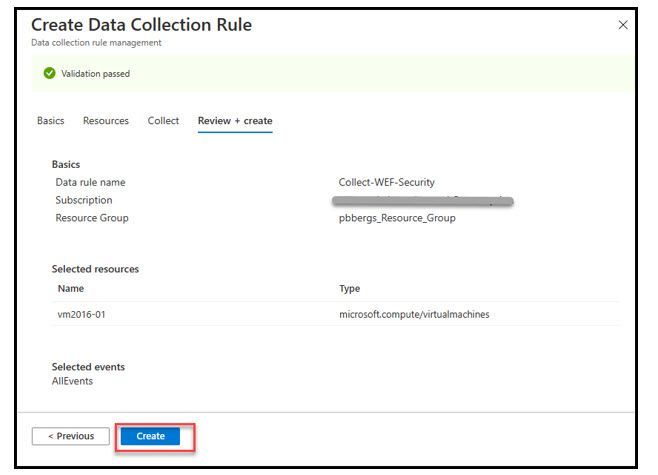
- Select “+Add data collection rule”
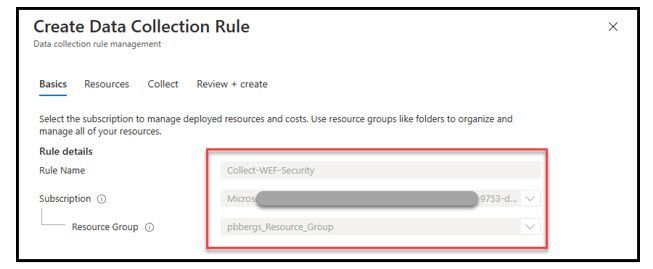
- On the “Basics” tab enter
- “Rule Name”, “Subscription” and “Resource Group”
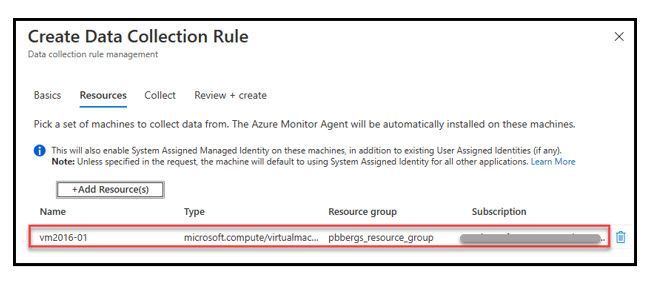
- On the “Resources” select the “+Add Resource(s)”
- Browse to the “Collector(s)” that will be capturing on-premises Security event logs
- Click the “Apply” button
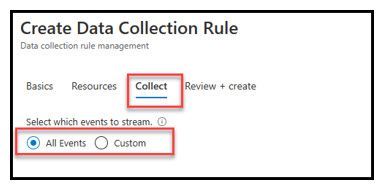
- On the “Collect” tab select the “+Add Resource(s)”
- Browse to the on-premises Data Collector (VM2016-01)
- Select the “Apply” button
- Choose if you want to send ALL security events or just a filtered list
- Click the “Next” button
- Click the “Create” button
Browse the LAW for Security Events
- Log onto the Azure portal:
https://portal.azure.com - Select Azure Sentinel
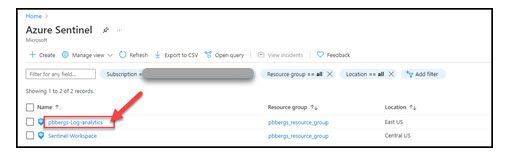
- Select the LAW
- Select the “Logs” blade
- Close the “Favorites” query page
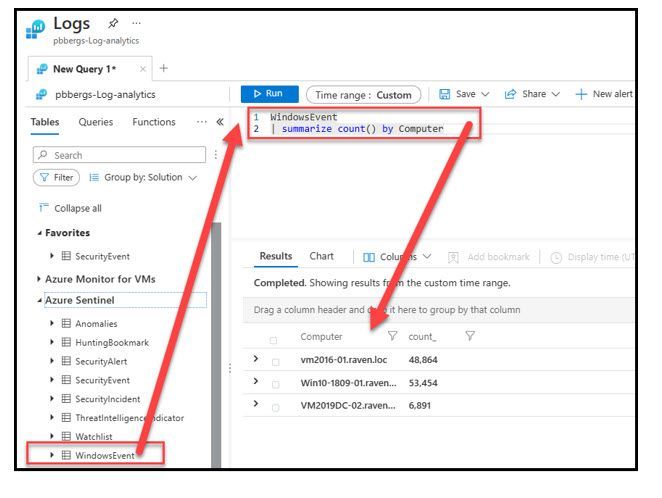
- To query the WEF logs imported into Microsoft Sentinel, the administrator can open a KQL query with the “WindowsEvent” table
- There are 3 hosts that are currently reporting to my LAW, which is defined within the WEC subscription(s)
- VM2016-01
- Win10-1809-01
- WV2019DC-02
This document won’t dive any deeper into KQL, if that is needed a separate document can be built to assist with filtering.
Hopefully this has provided you with some options to reduce costs and get your log data in a SIEM. I know Raven really appreciates me “Alerting” her to intruders in the backyard. :smiling_face_with_smiling_eyes:
References
- Windows Event Forwarding: Survival Guide - TechNet Articles - United States (English) - TechNet Wiki (microsoft.com)
- Setting up a Source Initiated Subscription - Win32 apps | Microsoft Docs
- Best practice of configuring EventLog forwarding performance - Windows Server | Microsoft Docs
- Use Windows Event Forwarding to help with intrusion detection (Windows 10) - Windows security | Microsoft Docs
- Azure Arc overview - Azure Arc | Microsoft Docs