We are excited to announce the support for Ddsv4 (General Purpose) and Edsv4 (Memory optimized) VM series with Azure Database for PostgreSQL – Flexible Server (Preview).
As you may know, the Flexible Server option in Azure Database for PostgreSQL is a fully managed PostgreSQL service that handles your mission-critical workloads with predictable performance. Flexible Server offers you with compute tier choices including Burstable compute tier for dev/test use cases, a General Purpose compute tier for running your small and medium production workloads, and a Memory Optimized compute tier to handle your large, mission-critical workloads. Flexible Server allows you to dynamically scale your compute across these tiers and compute sizes.
In addition to the existing DsV3 and EsV3 series of compute, you can now deploy using Ddsv4 and Edsv4 (V4-series) computes for your general purpose and memory optimized computing needs.
What are Ddsv4/Edsv4 VM series?
The Ddsv4 and Edsv4 VM series are based on the 2nd generation Intel Xeon Platinum 8272CL (Cascade Lake). This custom processor runs at a base speed of 2.5GHz and can achieve all-core turbo frequency of 3.4GHz. These compute tiers offer 50 percent larger and faster local storage, as well as better local disk IOPS for both Read and Write caching compared to the Dv3 and Ev3 compute sizes.
- Ddsv4 compute sizes provide a good balance of memory-to-vCPU performance, with up to 64 vCPUs, 256 GiB of RAM, and include local SSD storage.
- Edsv4 compute sizes feature a high memory-to-CPU ratio, with up to 64 vCPUs, 504 GiB of RAM, and include local SSD storage. The Edsv4 also supports a 20vCPU compute size with 160GiB of memory.
Ok. What are the benefits of running Flexible Server on v4-series?
- The V4-series compute sizes provide a faster processing power.
- V4-series also include high-speed local storage which are automatically used by PostgreSQL Flexible Server for read caching without requiring any user action.
So, depending on your workload and your data size, you could expect up to 40% performance improvement with V4 series compared to V3.
How about Flexible server V4-series pricing?
Please refer to the Azure Database for PostgreSQL – Flexible Server pricing page for detailed pricing. The V4-series flexible servers can be deployed using pay-as-you-go (PAYG or on-demand) pricing as well as reserved instance (RI) pricing. RI pricing offers up to 58% discount over PAYG pricing, depending on the compute tier and the reservation period.
I am currently running my server Postgres on V3-series. How can I migrate to V4-series?
You can simply scale your compute to any V4 compute size with a couple of clicks. From compute + storage blade (as illustrated in Figures 1, 2, and 3), you can simply modify your compute size to the desired V4 compute size. As scaling (compute migration) is an offline operation which would need couple of minutes of downtime in most cases, it is recommended that you perform scale operations during non-peak periods of your server. During the scale operation, your storage is detached from your existing server and gets attached to the new, scaled server. Flexible server offers a complete flexibility to scale your compute across all compute tiers and compute sizes at any time. You can either scale-up or scale-down the compute.
V4-series computes are only available with General Purpose or the Memory Optimized compute tiers. If you choose either of these tiers, then you’ll be able to select the new Ddsv4 compute size for General Purpose—or Edsv4 compute size for Memory Optimized compute tiers.
For example, to scale to General V4 compute size, from the "Compute + Storage" blade, choose the General Purpose tier.
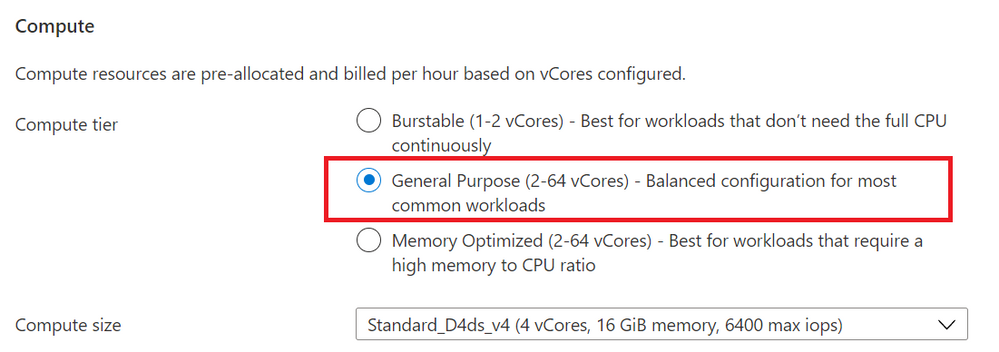
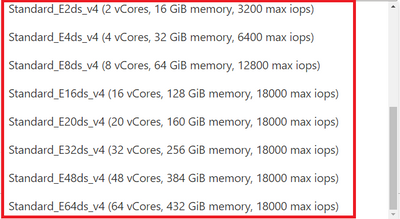
Then choose a General Purpose Ddsv4 compute size that suits your application needs.

Similarly, when you choose Memory Optimized compute tier shown in Figure 1, you can choose a Edsv4 compute size.
How do I transfer my existing reservations from V3 to V4?
If you are already using reserved instances with V3, you can easily exchange the reservations to the desired V4 compute, and you may just have to pay the difference in pricing depending on the compute tier.
Are these V4 compute tiers available in all regions?
Please see this list of regions for V3/V4 VM series availability.
All sounds good. What are the limitations?
- Currently, local disk caching is enabled for storage provisioned up to 2TiB, with plans to support caching for larger provisioned storage sizes in the future.
- The compute scaling is an offline operation and expect a couple of minutes of downtime. It is recommended to perform such scale operations during non-peak periods.
Where can I learn more about Flexible Server?
- The Flexible Server docs—which provide a great place to roll up your sleeves.
- This blog post: What is Flexible Server in Azure Database for PostgreSQL?
- We are always eager to hear your feedback so please reach out via email using Ask Azure DB for PostgreSQL.
Posted at https://sl.advdat.com/3DEeCfC
