Security Settings Management in Microsoft Defender for Endpoint is now generally available (3 min.)
Preventing data breaches and maintaining compliance are at the top of every organization’s agenda. It is essential for IT and security teams to develop a more cohesive partnership that embraces collaboration to enable business and drive future success.
Microsoft is privileged to sit at the intersection of IT and Security and continuously looks for opportunities to advance integration between security and IT management.
In late 2021, we announced that Microsoft Defender for Endpoint expanded its configuration management capabilities. This release empowered security teams to configure devices with their desired security settings without needing to deploy and implement additional tools or infrastructure. Made possible with Microsoft Endpoint Manager, organizations have been able to manage antivirus (AV), endpoint detection and response (EDR), and firewall (FW) policies from a single view for all enlisted devices.
Today, we are announcing that this capability is now generally available for Windows client and Windows server, supporting Windows 10, Windows 11, and Windows Server 2012 R2 or later.
Before you begin
This capability was designed for the following use cases:
- Managing devices traditionally out of scope for management because of support (OS Platform) or use case (servers in a network segment without management presence)
- Providing management capability to organizations that previously did not have access to tooling
Get started
Use the following recommended best practices to begin your endpoint security management journey with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint:
Configure your tenant
After verifying the tenant meets the pre-requisites, enabling the feature requires turning on relevant toggles both in Microsoft Defender for Endpoint and Microsoft Endpoint Manager. All these steps are documented here.
Note: Customers that will leverage Azure Active Directory Hybrid Join for a device identity may need to make updates to Azure Active Directory Connection (AAD Connect). These changes may include ensuring devices are ‘in-scope’ for device join, or additional configuration for Windows Server 2012 R2. Please review the documentation for more details.
Test the feature end-to-end
Step 1: Enable the feature in pilot mode in Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
Prior to enabling the feature for all OS platforms, we recommend testing the feature on a limited scope of devices by leveraging our “Pilot mode” capability. This will enable you to target specific devices to test Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Security Configuration Settings Management. You will need to tag the devices with the “MDE-Management” tag so that it gets managed by Microsoft Defender for Endpoint.
Step 2: Create a dedicated Azure Active Directory (AAD) Group
As our preview blog post outlined, devices will first establish a trust with Azure Active Directory. Once the device appears in AAD, it can be added to an AAD group.
As part of the testing of MDE Settings Management, our recommendation is that you create a dedicated AAD group for all devices enrolled to AAD via Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Security Configuration Settings Management. This can be done by creating an AAD group, using dynamic grouping capabilities, and based on the dedicated System Labels we’re adding to devices.
Step 3: Target a security policy from Microsoft Endpoint Manager
Using Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center, administrators can use the Endpoint Security blade to create antivirus (AV), endpoint detection and response (EDR), and firewall (FW) policies to be enforced on devices via Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Security Settings Management.
Create the policy of your choice, and when required to target it to an AAD group, select the AAD group you just created in step 2.
Step 4: Validate the policy assignment
Wait for the policy to be enforced on the device and view a success indication in the Microsoft Endpoint Manager portal. Note that policies are typically enforced within an hour after configuration. On the client, run the Get-MpPreference command utility to validate the settings have effectively been assigned.
Troubleshoot issues
Ran into issues? Getting an error in the device page of the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint portal? Our troubleshooting guide is here to help.
From the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint portal to the Client analyzer, we have made sure all your favorite troubleshooting tools will point to actionable recommendations so that devices encountering issues will succeed in this flow. We strongly recommend fixing any issues and becoming familiar with our troubleshooting capabilities prior to turning the feature on throughout the tenant.
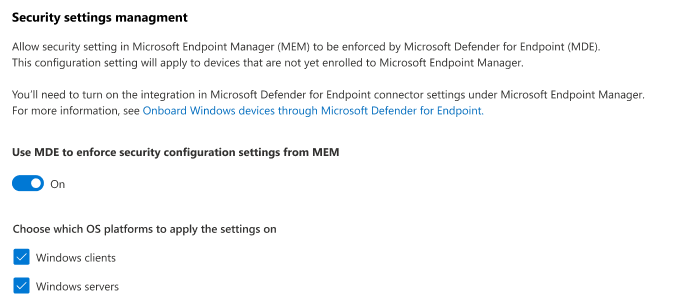
Enable Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Security Settings Management per OS Platform
Our end goal has always been for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint to independently identify unmanaged devices and bring them into management automatically thanks to Security Management for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. Once devices are enrolled, refer to the security settings management page located within the Microsoft 365 Defender portal and turn on the feature for the operating system platform you need.
After applying this configuration setting, Microsoft Defender for Endpoint will continuously monitor your environment for unmanaged devices that match the OS selection and target them with security policies.
What to expect next
We are working on expanding this capability to help cover more use case scenarios. Please reach out if you would like to share your experience or provide feedback regarding Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Security Settings Management!
Posted at https://sl.advdat.com/38p6827https://sl.advdat.com/38p6827